
Longitudinal antibody titers measured after COVID-19 mRNA vaccination can identify individuals at risk for subsequent infection
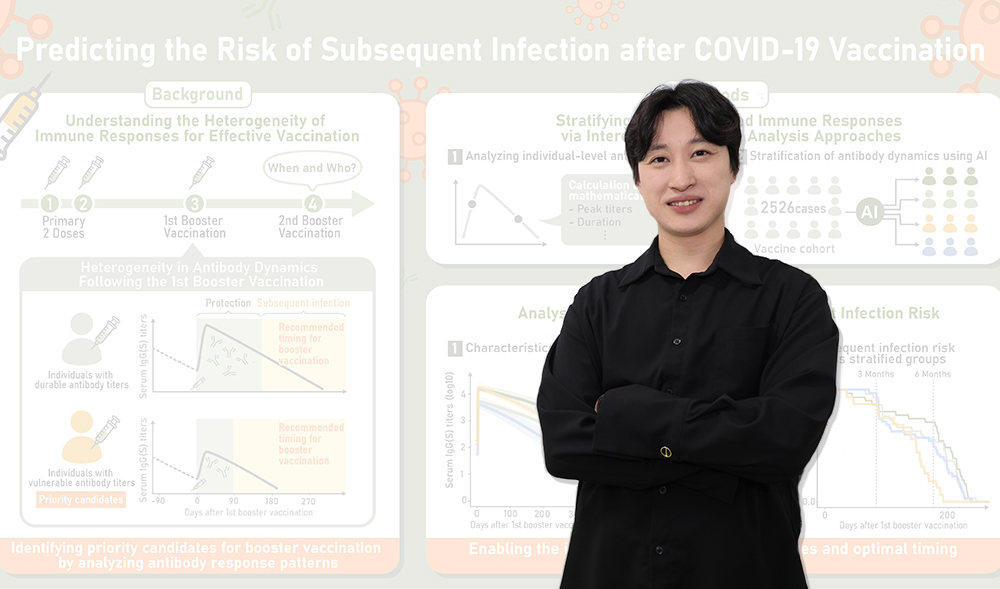
Although COVID-19 posed a major threat, the success of mRNA vaccines enabled rapid development and distribution, helping to control the pandemic. However, vaccine-induced immunity wanes over time, and large individual differences make it difficult to design optimal booster strategies. Identifying poor responders who fail to sustain antibody levels is therefore crucial for prioritizing revaccination.
In this study, we analyzed longitudinal antibody data from 2526 individuals in Fukushima (2021–2022) using mathematical modeling and machine learning. We identified three distinct antibody persistence patterns—durable, vulnerable, and rapid-decliner—and found that rapid-decliners tended to become infected earlier. This suggests that the ability to maintain antibodies, rather than high initial titers, may be more important for preventing early infection. Additionally, individuals who experienced breakthrough infections showed lower early spike-specific IgA levels after booster vaccination, indicating that IgA may serve as a useful marker for assessing breakthrough infection risk.
This approach provides valuable evidence for optimizing vaccine allocation and enhancing population-level immunity in future pandemics and the post–COVID-19 era.
- Author (Pusan National University): Hyeongki Park (School of Biomedical Convergence Engineering)
- Title of original paper: Longitudinal antibody titers measured after COVID-19 mRNA vaccination can identify individuals at risk for subsequent infection
- Journal: Science Translational Medicine
- Web link: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/scitranslmed.adv4214
- Contact e-mail: hkpark@pusan.ac.kr

 251125..........өҗмҲҳ1.jpg
(262KB)
251125..........өҗмҲҳ1.jpg
(262KB)