
PNU 리서치
- 메인으로 이동
- 연구/산학
- PNU 리서치
제약학과 이승락(사진) 교수 국제 공동연구팀이 지금까지 한 번도 보고되지 않은 새로운 화학 구조를 가진 항암 선도물질을 토양 박테리아로부터 발굴해, 천연물을 활용한 제약·바이오 제재 개발의 새 가능성을 열었다.
이승락 교수는 미국 프린스턴대학교(Princeton University) 연구진과 공동으로 토양 박테리아인 Streptomyces hiroshimensis(스트렙토마이세스 히로시멘시스)로부터 학계에 보고된 적 없는 새로운 화학 구조의 항암 선도물질 hirocidin A−C를 발굴했으며, 이 물질에서 대장암 및 난치성 유방암 세포에 유효한 저해 활성을 확인했다.
이 같은 연구 성과는 ‘Hirocidins, Cytotoxic Metabolites from Streptomyces hiroshimensis, Induce Mitochondrion-Mediated Apoptosis(Streptomyces hiroshimensis 유래 세포 독성 대사체인 Hirocidin의 미토콘드리아 매개 세포사멸 유도)’라는 제목의 논문으로 국제 학술지 『Angewandte Chemie - International Edition』에 보고돼 9월 1일자에 게재됐다.
- 논문 링크: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/anie.202405367
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.202405367
암은 전 세계적으로 주요 사망 원인 중 하나다. 그러나 기존 항암 치료법은 약물 내성, 비특이적 독성, 제한된 치료 효능 등 여러 문제점이 있어, 새로운 작용 기전을 가진 항암제 개발이 시급히 요구되고 있다.
천연물은 오랫동안 다양한 질병 치료에 사용돼 왔으며, 현재 임상에서 사용 중인 각종 약물도 천연물에서 유래한 경우가 많다. 이는 천연물의 독특한 화학 구조와 생물학적 활성에 기인한 것인데, 특히 미생물에서 유래한 새로운 천연물 탐색은 새로운 약물 개발에 필요한 혁신적인 구조를 제공할 수 있어 관심을 받고 있다.
이번 연구에서 규명된 hirocidins A−C는 Streptomyces hiroshimensis라는 미생물로부터 새롭게 발견된 이차대사산물이다. Streptomyces 속은 다양한 생리활성 물질을 생성하는 것으로 잘 알려져 있지만, 이번 연구에서는 이전에 보고되지 않았던 새로운 화합물이 발견됐다. 기존 연구들이 이미 알려진 물질의 구조 변형이나 유사한 계열에서 새로운 유도체를 찾는 데 중점을 뒀다면, 이번 연구는 전혀 새로운 화합물을 처음으로 규명한 점에서 의의가 크다.
hirocidins A−C는 대장암 및 난치성 유방암 세포에 대한 선택적 독성을 나타냈다. 일반적인 세포에도 독성을 미치는 기존의 항암제와는 달리, 암세포에 특이적으로 작용할 가능성을 보여주는 중요한 결과다. 특히, 난치성 유방암처럼 기존 치료제에 저항성을 보이는 암종에 대해 효과를 보인다는 점은 임상적 가치를 높이는 요소다.
또한, 이번에 규명된 화합물은 일반적인 식물에서 발견되는 물질과는 구별되는 매우 독특한 구조적 특징을 갖고 있다. 이는 합성으로 접근하기 어려운 독특한 구조여서 새로운 작용 기전을 제공할 가능성이 높다.
연구팀은 많은 연구자가 지나치기 쉬운 박테리아 액체 배양체의 펠렛에 주목해 항암 활성 추적 분리법 기반 신규 이차대사산물을 발굴했다. S. hiroshimensis에 대해 최적의 액체 배양 조건을 확립해 이를 기반으로 S. hiroshimensis 상층액, 펠렛 추출물의 대장암 및 난치성 유방암 세포에 대한 항암 활성을 평가하고, 그 후 항암 활성 추적 분리법을 적용해 hirocidins A−C를 포함한 총 5종의 신규 화합물과 9종의 기지 화합물 분리했다. 질량 분석기, 핵자기 공명 실험법, 계산 화학 등을 활용해 hirocidins A−C를 포함한 총 14종 화합물의 절대 화학 구조를 규명하는 데 성공했다.
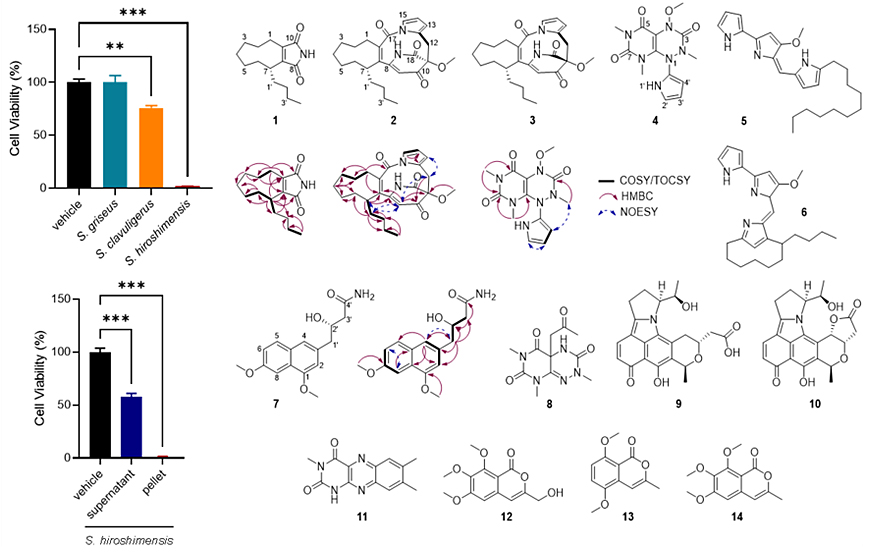
【S. hiroshimensis 배양액, 상층액, 및 펠렛 추출물의 항암 활성 평가(왼쪽-위, 아래)
항암 활성 추적 분리법 기반 S. hiroshimensis 유래 신규 이차대사산물 발굴(오른쪽-위, 아래)】
이번 연구에서 규명한 이차대사산물은 대장암 및 내성 유방암 세포에 대한 유의미한 항암 활성을 나타냈다. 이는 암 세포에 선택적으로 세포 독성을 유도해 내성 형태의 암 치료를 위한 새로운 치료 전략을 개발하는 데 활용될 수 있을 전망이다.
이 신규 화합물의 독특한 구조적 특성은 관련 화합물과 유사체에 대한 추가 연구도 기대하게 한다. 구조-활성 관계를 탐구하면 개선된 효능 또는 독성이 감소된 새로운 유도체를 발견할 수 있을 것으로 보인다.
이승락 교수는 “이번 연구는 미생물이라는 천연자원 소재로부터 신규 생리활성 물질 발굴의 가능성을 제시한 것으로, 천연물을 활용한 제약 및 바이오 관련 기업에 새로운 영감을 제시할 수 있다”고 말했다.
[Abstract]
Owing to millions of years of evolution, natural products have emerged with wide-ranging physiological functions and inspired chemists and biologists alike with their complex structures and therapeutic activities. Actinomycete bacteria, in particular, have offered an unparalleled source of antimicrobial and anticancer agents with vancomycin and mitomycin providing but two well-known examples of such therapeutics. Recent advances in DNA sequencing technologies coupled with bioinformatics indicate that the natural products discovered so far merely represent the tip of the iceberg as the products of most biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs) that can be observed in microbial genomes remain to be identified. Even microbes previously considered exhausted or drained have emerged as valuable reservoirs of untapped metabolites and, with the appropriate discovery methods, these strains can yield new and potentially useful compounds.
Motivated by this untapped potential and the possibility of finding new molecules from well-studied strains, we subjected established antimicrobial producers to antiproliferative assays against persistent cancer cell lines. We discovered five novel natural products including hirocidins A–C that form a new chemotype and are constitutively produced by Streptomyces hiroshimensis. Hirocidin A possesses a carbocyclic maleimide; its structure was established by spectroscopic analysis as well as a concise total synthesis route. Variants B and C contain a bridged azaheterocyclic backbone within a larger macrocyle. Hirocidins display promising cytotoxic activities and subsequent mode of action studies showed that they induce cell death by caspase-9-mediated apoptosis. Our work is in line with the notion that even well-trodden strains remain useful sources of new natural products. The discovery and total synthesis of hirocidin A will facilitate structure activity relationships to better understand and enhance its anticancer activity.
* Reference
- Authors (Pusan National University): Seoung Rak Lee (College of Pharmacy)
- Title of original paper: Hirocidins, Cytotoxic Metabolites from Streptomyces hiroshimensis, Induce Mitochondrion-Mediated Apoptosis
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/anie.202405367
- Journal: Angewandte Chemie - International Edition
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.202405367
