
PNU 리서치
- 메인으로 이동
- 연구/산학
- PNU 리서치

산업공학과 한준희(사진) 교수팀이 제한적인 환경에서 부족한 제조 설비 데이터를 AI(인공지능)를 활용해 추론, 최적의 생산 스케줄을 제공할 수 있는 프레임워크를 제안했다.
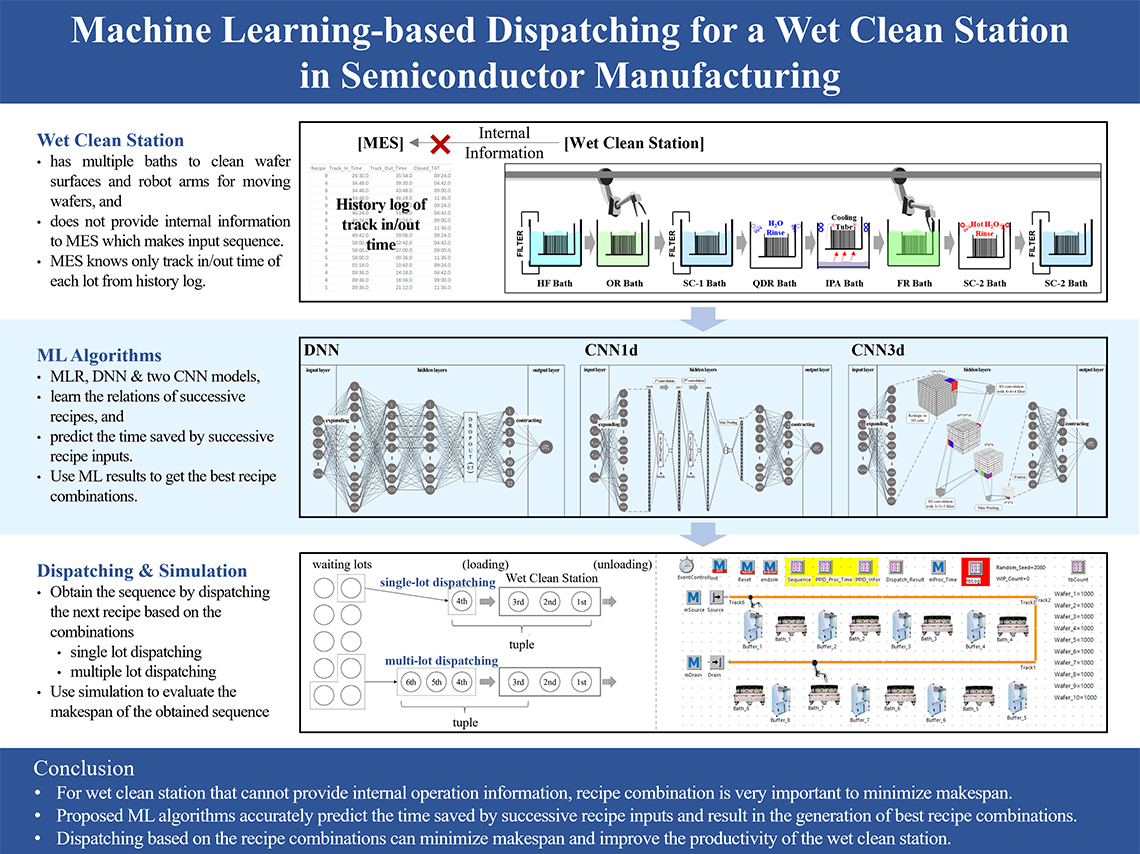
연구팀은 ‘Machine learning-based dispatching for a wet clean station in semiconductor manufacturing(반도체 세정 설비의 기계학습 기반 제품 투입 최적화)’ 제하의 논문을 통해 다양한 제품을 생산하는 제조 설비에서 제공하는 최소한의 정보를 활용해 AI 모델로 설비의 생산량을 예측하고, 이를 통해 최적의 생산 스케줄을 수립해 생산 계획을 최적화 할 수 있는 알고리즘을 제시했다.
이번 실험은 반도체 세정 공정에서 이뤄졌다. 반도체 칩을 만드는 기본 재료인 ‘웨이퍼’라는 얇은 판을 깨끗하게 세척하는 과정을 더 빠르고 효율적으로 만드는 방법을 연구했다.
웨이퍼 세척은 표면의 먼지, 오염 물질, 얼룩을 제거해 반도체의 성능과 품질을 향상시키기 위해 여러 가지 화학 물질과 물로 씻는 공정이다. 이 과정에서 로봇 팔이 웨이퍼를 옮기는데, 세척 시간이나 순서가 제품마다 달라 최적화 시 생산성 향상을 기대할 수 있다. 그러나 문제는 세척 과정을 최적화하기 위한 시간이나 순서 등 세부 정보를 알기 어렵다는 점이다. 주어진 정보는 언제 웨이퍼가 세척기에 들어가고 나왔는지를 기록한 로그 정도다.
연구팀은 이러한 제한된 데이터를 활용하기 위해 AI 기술을 사용했다. AI 모델을 훈련시켜 웨이퍼 세척 시간이 어떻게 달라지는지 예측하고, 이를 바탕으로 웨이퍼를 가장 효율적으로 배치하는 방법을 개발했다.
실험 결과, 이 방법이 기존의 수학적 계산 방식(CPLEX)보다 더 빠르고 실용적인 해결책을 제공한다는 것을 확인했다. 이를 통해 웨이퍼를 더 많이 세척할 수 있게 되어 공장 생산성 향상을 기대할 수 있다.
【기계학습을 이용한 설비의 생산 계획 최적화 방법론】
이번 연구에서 대상으로 삼은 반도체 세정 설비뿐만 아니라, 제조업에서 활용하고 있는 다양한 제조 설비는 설비에서 제공하는 데이터를 활용해 최적의 생산 스케줄을 도출하는 것이 아주 중요하다.
기존 연구에서는 생산 최적화를 위해 필요한 데이터가 모두 있다는 가정하에 이를 활용한 연구들이 주를 이뤘다. 그러나, 실제 현장에서는 생산을 위해 필요한 데이터가 모두 수집되지 못해 기존의 연구 방법론을 사용하는 데 한계가 존재한다. 이번 연구에서는 다양한 제품을 생산하는 제조 설비에서 제공하는 최소한의 정보를 활용해 AI 모델을 통해 설비의 생산량을 예측한다. 이를 통해 최적의 생산 스케줄을 수립해 생산성을 최대화 할 수 있다.
이러한 방법은 데이터의 수집이 제한적인 다양한 상황에서 응용될 수 있다. 복잡한 내부 설비의 움직임을 가지는 제조 설비 혹은 데이터의 수집에 한계가 있는 중소기업의 제조 설비에도 응용할 수 있다는 점에서 의미가 크다.
한준희(제1저자) 교수는 “이번 연구는 데이터의 수집이 제한적인 설비에서 부족한 정보를 유추하고, 이를 기반으로 생산성을 개선하는 AI 기반 알고리즘을 개발했다는 데 의미가 있다”며 “개발한 알고리즘은 데이터 수집이 충분하지 않은 다양한 제조 환경에 적용해 더 효과적인 생산 계획을 수립하는 데 큰 도움이 될 것”이라고 설명했다.
한편, 이번 연구는 중소벤처기업부 재원의 스마트제조기술개발 사업의 지원을 받아 강원대·울산대 연구진과 공동으로 수행됐다. 해당 논문은 Operations Research & Management Science(운영 연구 및 경영 과학) 분야와 Engineering(공학), Industrial(산업) 분야의 최우수 국제 저널인 『Journal of Manufacturing Systems』 12월호에 게재됐다.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmsy.2024.09.018
[Abstract]
The concept of cyber manufacturing has become a critical element in semiconductor fabrication environments, where automation and systemization are integral, for addressing the growing complexity of processes and facilitating predictive capabilities through data integration. This study deals with the dispatching problem to minimize makespan at a wet clean station in semiconductor fabrication using artificial intelligence-enabled manufacturing control techniques. The wet clean station is comprised of sequential chemical and rinsing baths for cleaning wafer lots and multiple robot arms for lot handling. In the station, wafer lots are sequentially immersed in several baths for cleaning to eliminate residual contaminants and stains that cause defects on wafer surfaces. The station can process various types of products, and the specific order of immersion differs depending on the product type. Unlike typical dispatching problems, the information required for dispatching, such as processing times and sequences inside the station, is not available. The only available data are historical logs that record when each lot enters and leaves the station. However, even when cleaning the same product type, the duration that lots spend in the station may vary based on the combination of product types being cleaned simultaneously and the settings of the station. Thus, using the time records, this study proposes a dispatching method based on machine learning models (multiple linear regression, deep neural network, and convolutional neural network). The proposed algorithms were evaluated and verified by comparing them with CPLEX solving a mixed integer programming and dispatching methods used in a semiconductor fab in Korea. Through this experiment, we observed that the proposed models can provide dispatching solutions that are practical and effective in a rapidly changing production setting. These models have the potential to enhance the capacity of a wet clean station and will contribute to artificial intelligence-based manufacturing system control.
* Reference
- Authors (Pusan National University): Jun-hee Han (Department of Industrial Engineering)
- Title of original paper: Machine learning-based dispatching for a wet clean station in semiconductor manufacturing
- Journal: Journal of Manufacturing Systems
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmsy.2024.09.018
- Lab website: https://sites.google.com/view/pnusmartfactorylab/home
